Blocked ears are one of the most common reasons patients contact Pro Ear Clinic. The sensation can range from mild fullness to significant hearing loss, pressure, ringing, or discomfort. For some people it comes and goes, while for others it persists for weeks and starts to affect daily life, communication, and confidence.
The challenge is that blocked ears are a symptom, not a diagnosis. Earwax build-up is a frequent cause, but it is far from the only one. Congestion, infections, and pressure problems within the ear can all create a blocked feeling, and each requires a different approach to treatment.
This guide explains the most common causes of blocked ears, how to recognise the difference between them, and when professional assessment and treatment is recommended.
Wax Build-Up (Cerumen Impaction)
The Most Common Cause of Blocked Ears
Earwax build-up is the number one cause of blocked ears seen in clinic. Wax is produced naturally to protect the ear canal, trap debris, and prevent infection. Problems occur when wax does not clear on its own and becomes compacted.
Wax build-up is more likely if you:
- Use cotton buds or earplugs
- Wear hearing aids
- Have narrow or curved ear canals
- Produce drier or thicker wax
- Have frequent ear infections
- Are over 60 (wax becomes harder with age)
When wax becomes impacted, it can completely block sound from reaching the eardrum, causing:
- Reduced or muffled hearing
- A feeling of fullness or pressure
- Crackling or popping sounds
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Dizziness in some cases
If you are experiencing ringing alongside blockage, read our detailed guide: Can Earwax Cause Tinnitus? (internal link).
How Wax-Related Blockage Is Treated
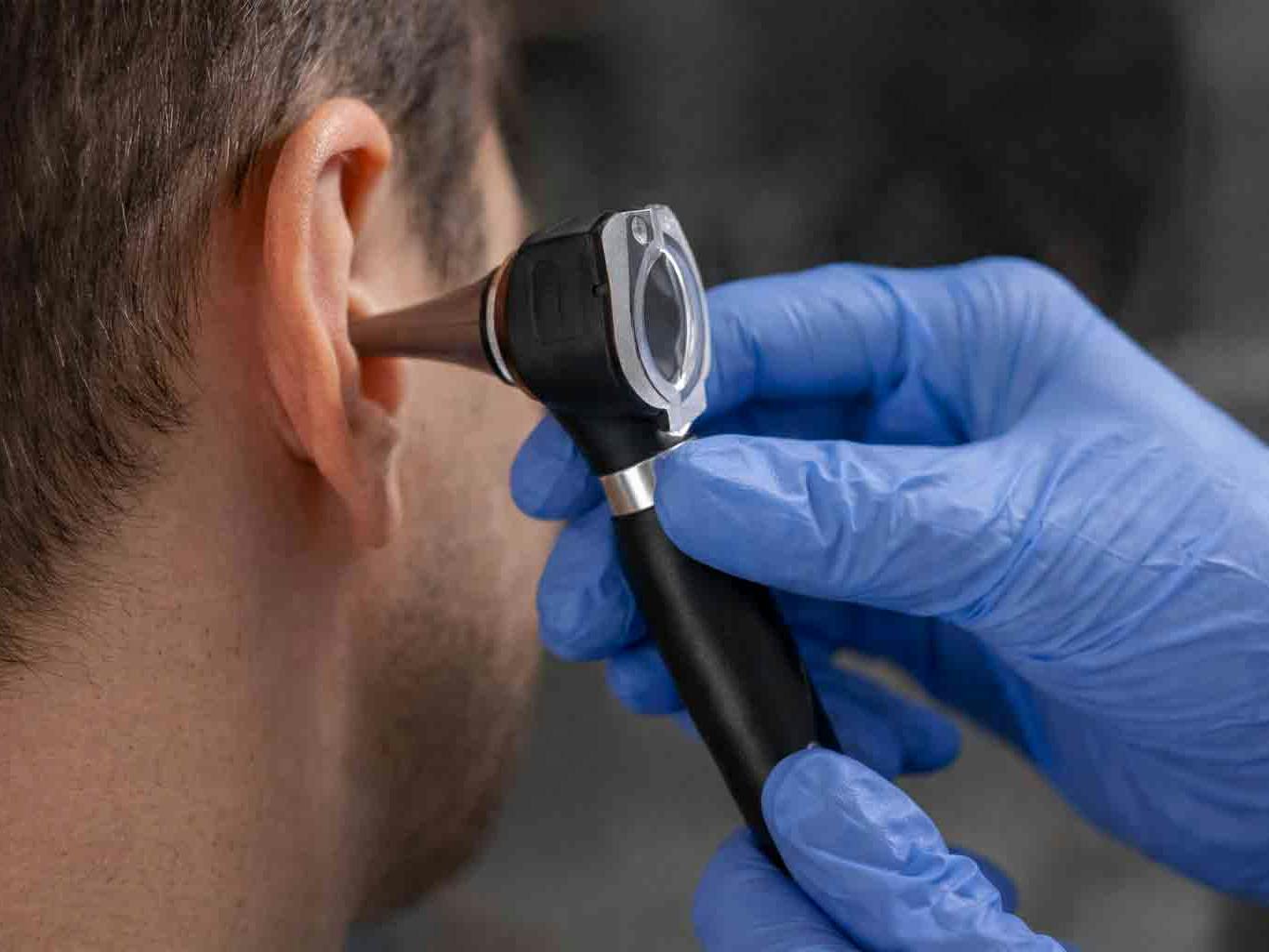
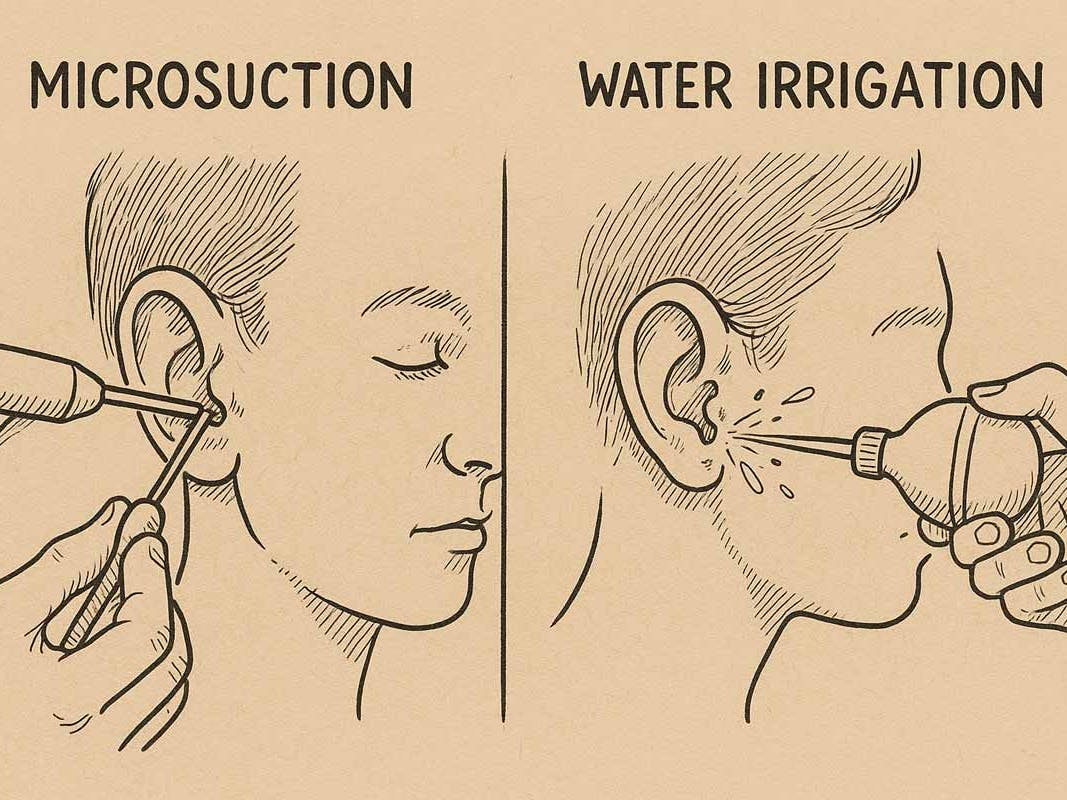
Professional removal is the safest and most effective option. At Pro Ear Clinic, this is usually done using microsuction, which removes wax under direct vision without water.
Over-the-counter drops may help soften wax, but they often do not remove blockages on their own, especially if the wax is hard or deep.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
A Common Non-Wax Cause of Blocked Ears
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. Its job is to equalise pressure and allow fluid to drain. When it doesn’t open or close properly, pressure builds up behind the eardrum.
This causes a blocked or “underwater” sensation, often described as:
- Ear fullness without hearing loss
- Popping or clicking
- Pressure changes when swallowing or yawning
- Symptoms worse during flights or altitude changes
ETD is commonly triggered by:
- Colds and flu
- Sinus infections
- Allergies
- Nasal congestion
- Acid reflux
Unlike wax, ETD cannot be fixed by ear cleaning, which is why examination is essential before treatment.
Congestion and Sinus-Related Blockage
Why Your Ears Feel Blocked During a Cold
When you have a cold, flu, or sinus infection, inflammation and mucus can affect the Eustachian tubes. This leads to pressure imbalance and fluid retention behind the eardrum.
Blocked ears caused by congestion often feel:
- Worse in the morning
- Worse when lying down
- Accompanied by a blocked nose or facial pressure
- Temporary and fluctuating
In these cases, earwax removal alone will not solve the problem. Treatment focuses on resolving nasal congestion and inflammation.
If symptoms persist beyond a few weeks or are one-sided, assessment is recommended.
Ear Infections
Blocked Ear vs Infection: Knowing the Difference
Ear infections can cause blockage, but they are usually accompanied by other symptoms. These may include:
- Pain or aching
- Discharge from the ear
- Swelling or redness
- Fever
- Hearing changes
- Sensitivity to touch
Infections may affect the outer ear (otitis externa) or the middle ear (otitis media). Both can cause swelling and fluid build-up, leading to a blocked sensation.
It is important not to attempt wax removal if infection is suspected, as this can worsen symptoms.
To understand the difference more clearly, read: Ear Infection vs Blocked Ear (internal link).
When Should You See a Clinician?
Many people delay treatment, hoping blocked ears will resolve on their own. While this can be appropriate in some cases, professional assessment is recommended if:
- Symptoms last more than 1–2 weeks
- Hearing is significantly reduced
- One ear feels blocked but not the other
- You experience ringing, dizziness, or pain
- Symptoms worsen instead of improving
- You wear hearing aids
- You have a history of ear problems
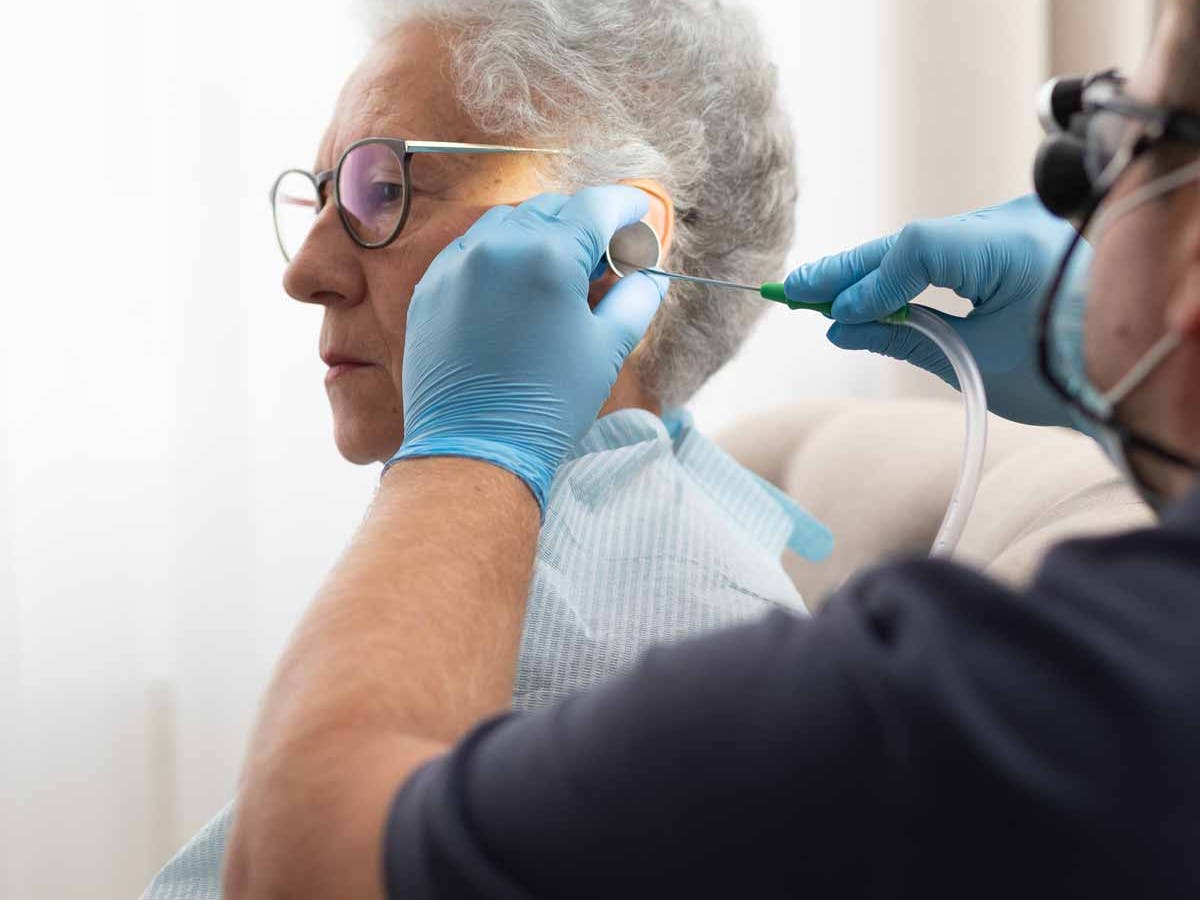
At Pro Ear Clinic, we always examine the ear first using otoscopy before recommending any treatment. This ensures the correct cause is identified and the appropriate solution provided.
Treatment Options for Blocked Ears
1. Microsuction Earwax Removal
If wax is the cause, microsuction is the safest and most effective treatment. It:
- Removes wax under direct vision
- Does not use water
- Is suitable for sensitive ears
- Provides immediate improvement in most cases
Microsuction is appropriate for clinic appointments and home visits across Bristol, including Audley Redwood Village.
2. Medical Management for ETD and Congestion
For non-wax causes, treatment may include:
- Nasal sprays
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Steam inhalation
- GP or ENT referral if needed
Removing wax when it isn’t the cause will not relieve symptoms, which is why assessment matters.
3. Infection Treatment
If infection is identified, wax removal is usually postponed. Treatment may involve:
- Ear drops
- Antibiotics (if bacterial)
- Anti-inflammatory medication
Once the infection resolves, wax removal can be safely carried out if required.
Why Self-Treatment Often Makes Blocked Ears Worse
Many patients try to fix blocked ears themselves using cotton buds, ear candles, or repeated drops. Unfortunately, these often:
- Push wax deeper
- Irritate the ear canal
- Cause inflammation
- Delay correct diagnosis
Cotton buds are one of the leading causes of impacted wax seen in clinic.
Professional assessment prevents unnecessary discomfort and repeat visits.
Blocked Ears and Hearing Aids
Hearing aid users are particularly prone to wax build-up. The presence of a hearing aid:
- Prevents natural wax migration
- Compresses wax deeper into the canal
- Increases moisture and warmth
Regular ear checks and professional cleaning help maintain hearing aid performance and prevent sudden blockage.
How Pro Ear Clinic Helps
At Pro Ear Clinic, blocked ears are assessed and treated with a patient-centred, clinical approach. Every appointment includes:
- Full ear examination
- Clear explanation of findings
- Appropriate treatment recommendations
- Gentle, safe techniques
- Advice to prevent recurrence
We treat adults and children (where appropriate) and offer both clinic-based and home visit appointments across Bristol.
Book an Assessment or Treatment
If your ears feel blocked, reduced hearing is affecting your day-to-day life, or you are unsure of the cause, professional assessment is the safest next step.
👉 Book your earwax removal or assessment appointment here.
Early treatment often provides immediate relief and prevents complications.
Book your Appointment
Your Ears. Our Care.
Wherever You Are in Bristol.
We provide professional ear wax removal in the comfort of your own home across the Bristol area.
Appointments are limited, secure your spot online today.
Need care home visits or something else? Visit our services page for more options.